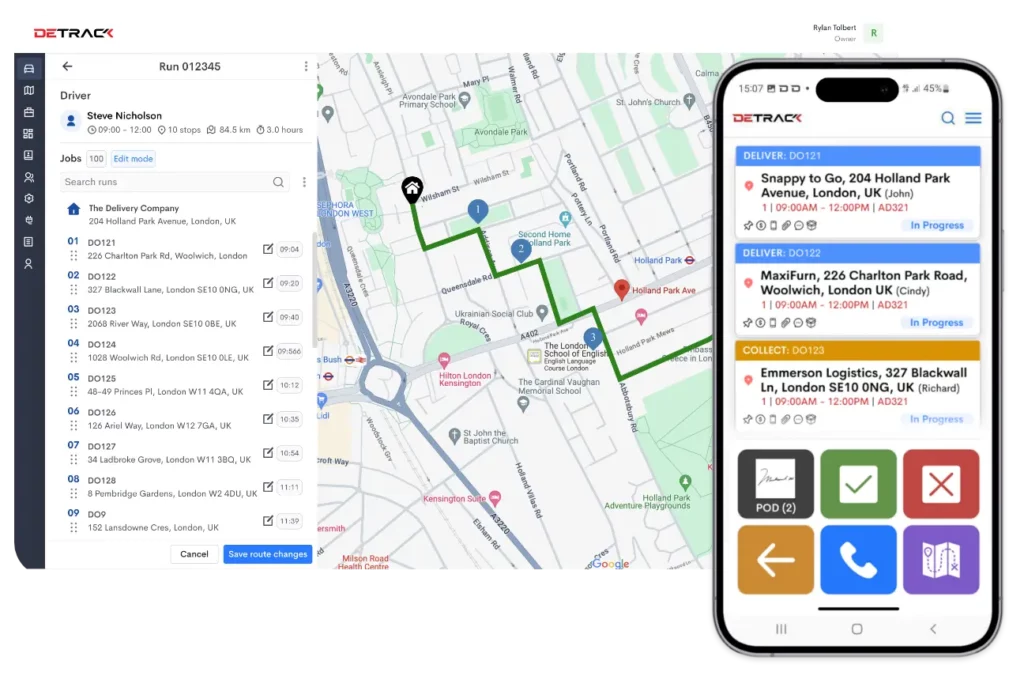
Route optimization has become an essential part of logistics, especially at a time when customers expect fast and accurate delivery. The last mile, which represents the most costly phase of the delivery process, requires effective planning and advanced tools to enable companies to meet these demands.
Delivery companies are using advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence and predictive models, to creation of optimised routes. These solutions allow drivers to minimise unnecessary stops, reduce costs and improve customer satisfaction at the same time. Strategically located warehouses and efficient traffic management play a key role in reducing time and financial losses.
The Importance of Route Optimization in Logistics
Route optimization is a fundamental element of successful logistics. It enables companies to reduce transport costs, shorten delivery times and increase customer satisfaction through more accurate delivery. The use of modern technologies such as predictive models or GPS systems helps to improve planning and reduce delays in deliveries.
Companies have the ability to analyse data from transport routes in real time. This process reveals bottlenecks, such as inefficient stops or congested areas, and then manages them by optimising transport routes or selecting alternative options. This approach maximises vehicle capacity and eliminates unnecessary journeys.
Studies show that last mile delivery accounts for up to 53 % of the total logistics cost. It is therefore essential to optimise routes at this stage. Accurate delivery routes are made using algorithms that take into account traffic, distance and customer preferences, reducing overall costs and saving time.
Improved warehouse segmentation also plays an important role in optimisation. If warehouses are located close to major transport hubs, transport times are reduced and deliveries are more reliable. This leads to a more efficient use of resources and a reduction in the negative environmental impact, for example through shorter routes or eco-friendly modes of transport such as electric vehicles.
Businesses that use optimised routes minimise the risks associated with delays and unexpected problems, thus ensuring happier customers and a better market position.
Key Strategies for Route Optimization
Efficient delivery route planning brings benefits such as lower costs, faster delivery and happier customers. Optimised routes help companies eliminate inefficient practices and use resources more efficiently.
Use of Artificial Intelligence and Algorithms
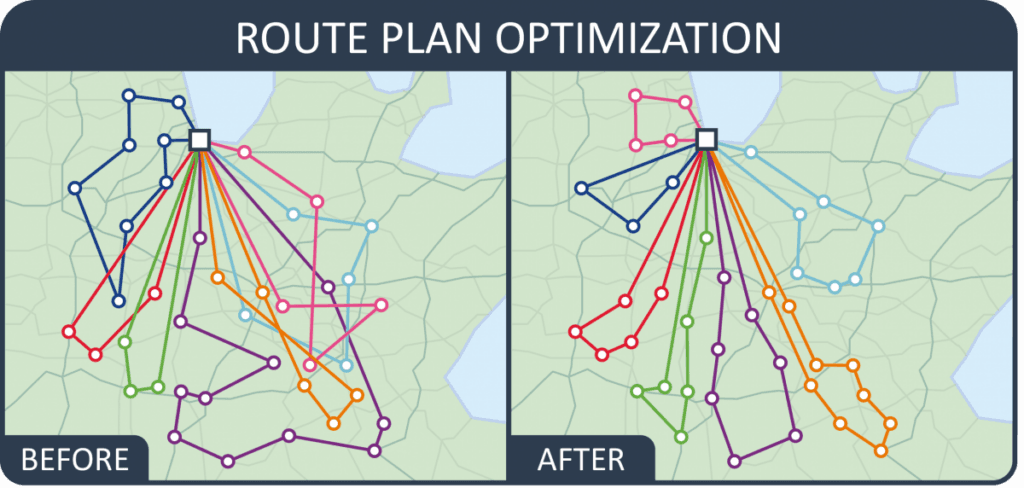
Artificial intelligence (AI) and algorithms allow delivery companies to analyse vast amounts of data and design solutions to optimise routes. AI can identify the fastest and most economical routes, taking into account factors such as traffic, distance and weather conditions.
AI-powered solutions can constantly re-evaluate existing routes in real time. This allows businesses to react to sudden changes such as congestion or delays without negatively impacting delivery times. For example, AI systems that prioritize delivery based on the urgency of shipments achieve attractive results.
In addition, autonomous algorithms can predict demand at specific locations, allowing for better resource distribution. In this way, the risk of incorrect decisions leading to unnecessary transfers or delays can be reduced, increasing the overall efficiency of the operation.
Predictive Analysis And Planning
Predictive models allow companies to plan delivery routes based on historical data and trends. These models help to better estimate order volumes, expected delivery times and future customer requirements.
Combining predictive analytics with data sources such as GPS data and IoT devices creates accurate predictions about the movement and condition of vehicles. Companies can avoid situations where vehicles remain idle or are used inefficiently. For example, scheduling deliveries in sparsely populated areas optimizes costs and minimizes mileage.
Predictive systems also detect seasonal fluctuations, such as higher demand during the holidays, creating an opportunity to adjust routes in a timely manner. In this way, delivery coordination errors are minimized, improving the reliability of the delivery network.
Consolidation of Delivery Points
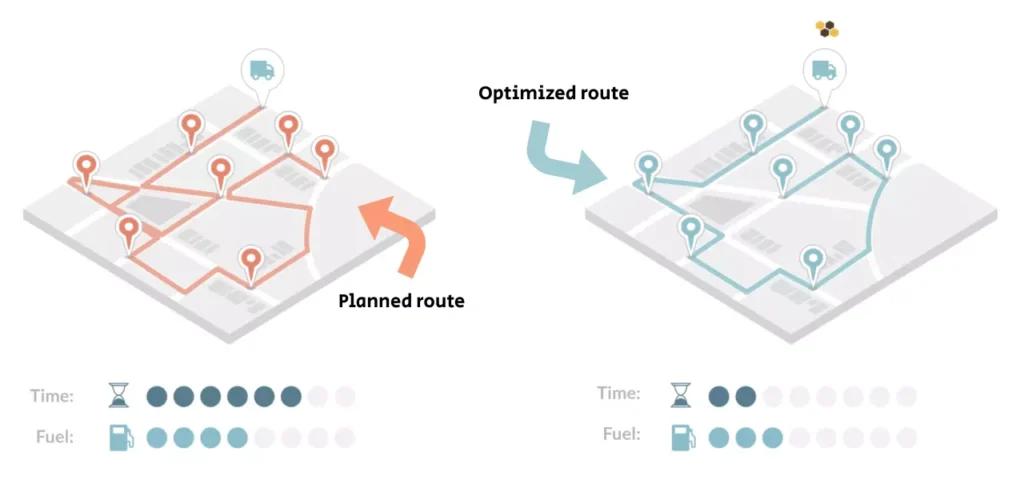
Consolidating the delivery process combines multiple shipments into a single route, making efficient use of vehicle capacity. Group delivery to geographically close areas reduces the number of trips and fuel costs.
Point consolidation uses intelligent software tools to group orders based on similar characteristics such as distance and delivery time. Warehouses and distribution centres located in strategic locations allow for easier logistics and lower transit times.
This approach also includes reverse logistics, where the pick-up of returned shipments is combined with scheduled delivery. This also allows for efficiency in the case of return distribution, saving companies time and costs. The integration of this method leads to reduced emissions and greener delivery.
Technologies Used in Route Routing
Delivery route optimization uses different modern technologythat improve planning accuracy and transport efficiency. These systems help delivery companies respond to current needs and reduce delivery times.
GPS And Tracking Systems
GPS technology is the basis for efficient route planning in logistics. It enables real-time tracking of vehicle locations and helps to optimise delivery routes based on current traffic conditions. For example, systems such as GPS Trackers provide information on vehicle location, traffic and speed limits.
Vehicle tracking also helps reduce fuel costs. Vehicles can avoid congested areas or roads in poor condition, effectively reducing fuel consumption. This leads to more sustainable transport.
In addition, GPS systems have proven to increase delivery accuracy. Clients receive information about the arrival time of their shipment, which increases their satisfaction. Tracking devices also offer records that companies use in retrospective analysis to improve logistics processes.
Integrated Logistics Application Software
Logistics process management software plays a key role in optimising transport. These systems integrate all steps, from route planning to vehicle monitoring, into one comprehensive solution. For example, AI-enabled systems can predict delivery times based on historical data and current conditions.
Modern applications enable the creation of efficient delivery schedules. They take into account traffic, distances and order volume when calculating the optimal route. The software tools also assist in allocating individual shipments between vehicles, thereby reducing the number of unused capacities.
These systems provide data on the performance of the transmission network: from analysing delays to optimising future distribution. This ensures continuous improvement of logistics performance. Companies that implement such solutions achieve lower overall transport costs and improved flexibility.
Mobile Apps for Drivers and Employees
Mobile apps are an essential tool for connecting drivers and logistics management. They provide the necessary information on planned routes, delivery changes and updates on traffic conditions. For example, drivers can instantly inform dispatch of unexpected obstacles via the app.
These applications speed up the exchange of data between teams. If there is a road closure, drivers receive new instructions without the need for manual intervention. Training on how to use the apps is minimal, saving time during deployment.
In addition to route and obstacle information, the apps also include performance monitoring features. Driving style records help to assess drivers and identify areas for improvement. Such systems increase the efficiency of the entire delivery network and minimize the risk of errors.
Benefits of Route Optimization for Delivery Companies
Route optimization brings significant improvements for delivery companies. The combination of modern technology and efficient strategies reduces costs, speeds up processes and improves customer experience.
Reduced Fuel and Maintenance Costs
Optimised routes contribute significantly to savings in fuel and vehicle maintenance. Technologies such as GPS and analytical algorithms enable route planning with lower fuel consumption. For example, selecting shorter and less congested routes reduces consumption by 10-15 %, which is particularly critical for fleets with high daily mileage.
Real-time monitoring helps prevent vehicle wear and tear by informing drivers about road conditions and identifying potential problems such as potholes or inefficient stops. According to data from the American Transportation Research Institute, fuel costs are a major item in vehicle operating expenses. Automated driving systems not only reduce these expenses, but also optimize overall vehicle wear and tear.
Increased Customer Satisfaction

Accurate and efficient delivery routes ensure faster delivery, leading to higher customer satisfaction. The average customer expects delivery to be not only on time, but also convenient. Predictive models analyse historical data to accurately forecast delivery times and take into account factors such as traffic and weather conditions.
Companies that offer flexible delivery options, including alternative locations or exact times, differentiate themselves from the competition. For example, extending customer support through real-time tracking of shipments increases customer confidence by providing information on the current status of an order. Customers tend to prefer reliable suppliers, leading to higher repeat purchase rates.
Environmental Benefits And Sustainability
Optimising transport has a positive impact on the environment. Shorter routes and fewer stops significantly reduce carbon dioxide emissions. Electric vehicles and eco-friendly packaging are becoming key components of modern logistics strategies.
Distribution businesses often explore ways to reduce waste through optimising transport and consolidating shipments. Strategic delivery planning can reduce emissions by 20 % if AI-based technologies are used along with sustainable solutions such as the use of recyclable packaging materials. Green measures not only contribute to environmental protection, but also improve corporate reputation.
Challenges in Implementing Route Optimization
Optimising delivery routes faces several challenges that can affect the efficiency of logistics processes. The most common obstacles include unpredictable demand and technological constraints.
Irregularities in Dopyte and Operation
Irregularities in customer demand and traffic represent a significant barrier to efficient route planning. Seasonal fluctuations, rush orders or specific time requirements of customers can make optimisation difficult. For example, during the holidays, surges in orders can exceed the normal capacity of delivery networks, creating delays.
Another problem is unpredictable factors such as traffic accidents, construction work or changes in traffic regulations. Delivery companies need to be prepared to respond to changes in real time to minimise the impact of these issues on delivery times.
Businesses with larger vehicle fleets face additional challenges such as proper driver coordination and even load distribution. If accurate demand forecasting is not available, some routes may be overloaded while others are underutilised. Effective resource allocation requires extensive analysis of historical data and depends on the availability of advanced analytical tools.
Technological Barriers
Technological constraints are another major issue for route optimisation. Legacy logistics systems or incompatibilities between different software solutions can slow down the implementation of modern technologies. For example, some companies still use outdated manual procedures for route planning, which are time-consuming and error-prone.
Lack of investment in new technologies, such as data analysis tools or artificial intelligence, can hinder effective optimisation. Predictive models and algorithms require a robust technological foundation and high accuracy of input data.
Delivery companies also have to grapple with the complex process of integrating tracking devices, GPS technology and mobile apps. If the systems cannot communicate in real time, delays or route planning errors can occur.
In addition, some companies face data security issues. Logistics systems process sensitive information such as customer addresses or order data, which increases the risk of cyber-attacks. A common solution is to invest in encryption mechanisms and regular software updates.
The Future of Route Optimization
The future of logistics routes will be driven by advanced technologies. Automated systems and artificial intelligence are transforming transport and delivery management to a whole new level.
Automation And Autonomous Vehicles
Automation brings increased efficiency to delivery processes. For example, autonomous deliveries with automated vehicles reduce labor costs and minimize human error. These technologies are already being tested by leading logistics companies in various countries and are expected to cover up to 60 % delivery needs by 2030.
An example of the integration of autonomous technologies is the use of drones for rapid delivery in urban areas. Drones can reduce delivery time by 50 % compared to traditional methods. In villages with weaker road network coverage, autonomous vehicles can replace conventional transport to some extent.
Robotic systems in warehouses speed up the creation and sorting of loads, which means up to 25 % increase in productivity for large enterprises. Autonomous robots quickly identify specific packages and delivery routes, speeding up vehicle deployment.
One of the biggest challenges remains the regulation and safety of autonomous technologies. Countries are gradually adapting legislation, but the deployment of these systems still runs into bureaucratic complexity. Nevertheless, increasing pressure to optimise transport is driving research and development in this area forward.
Development of Intelligent Transport Systems
Intelligent transportation systems employ AI and sensors to collect real-time data. This information includes traffic congestion, accidents and weather conditions. For logistics companies, this means the ability to make immediate changes to routes based on the current situation.
Linking GPS systems with traffic management allows for improved route planning accuracy and reduced costs. Dynamic traffic management through data-driven traffic lights has already been introduced in cities with high population density. This has reduced the delay of delivery network vehicles by 30 %.
"Smart roads" are also an important part of this, with built-in sensors to record and transmit information about road conditions. This is useful not only for improving the efficiency but also the safety of transport. Traffic managed in this way reduces the likelihood of traffic collisions.
Companies are investing in integrating IoT technologies with their logistics systems to enable more accurate monitoring of product status, especially when transporting sensitive goods such as pharmaceuticals. The use of IoT can reduce financial losses associated with shipment damage by up to 20 %.
The combination of autonomous vehicles and intelligent transport systems will help companies in the coming years not only to shorten delivery routes, but also to increase customer satisfaction, which is crucial in a competitive environment.
Conclusion
Optimising delivery routes is essential for modern delivery companies facing increasing demands for speed and accuracy. Leveraging advanced technologies and efficient strategies not only reduces costs, but also improves sustainability and customer satisfaction.
Firms that invest in innovation gain a competitive advantage and adapt better to dynamic market conditions. With the growing emphasis on green solutions and automation, optimised routes will be a key success factor in logistics.